What Is A Domain Biology Definition
Archaea bacteria and eukarya.
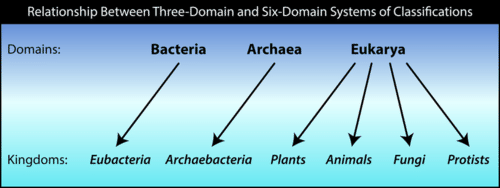
What is a domain biology definition. According to the three domain system of carl woese introduced in 1990 the tree of life consists of three domains. In biological taxonomy a domain also superregnum superkingdom empire or regio is the highest taxonomic rank of organisms higher than a kingdom. All life that has a cell nucleus and eukaryotic membrane bound organelles is included in eukar.
According to the modern system called the three domain system created by carl woese in 1990 there are three. A domain is a network of computers and devices that are controlled by one set authority and that have specific guidelines. In biological taxonomy a domain also superregnum superkingdom or empire is a taxon in the highest rank of organisms higher than a kingdom.
Eukaryotes bacteria and archaea. The three domains are archaea bacteria and eukarya. Glossary of biology terms.
These classifications are very broad and each of the three categories is broken down into more specifi. For the term domain may also exist other definitions and meanings the meaning and definition indicated above are indicative not be used for medical and legal or special purposes. Superkingdom the highest level of classification of living organisms.
Domain or its synonyms is the most inclusive of these biological groupings. Meaning and definition of domain. In biology a domain is the highest possible classification of organisms.
Comparing rrna structure is especially useful. In biology a domain refers to the largest of all groups in the classification of life. Domain name system dns servers translate a domain name.