Functional Domain Definition Biology

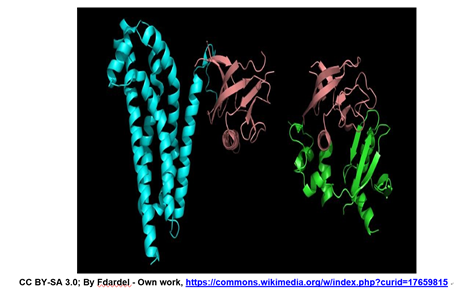
In dper intermolecular interaction of the two pas domains pas a and pas b is necessary for per homodimer formation.
Functional domain definition biology. In biology a domain refers to the largest of all groups in the classification of life. Conserved domain search service cd search identifies the conserved domains present in a protein sequence. The first two are all prokaryotic microorganisms or mostly single celled organisms whose cells have no nucleus.
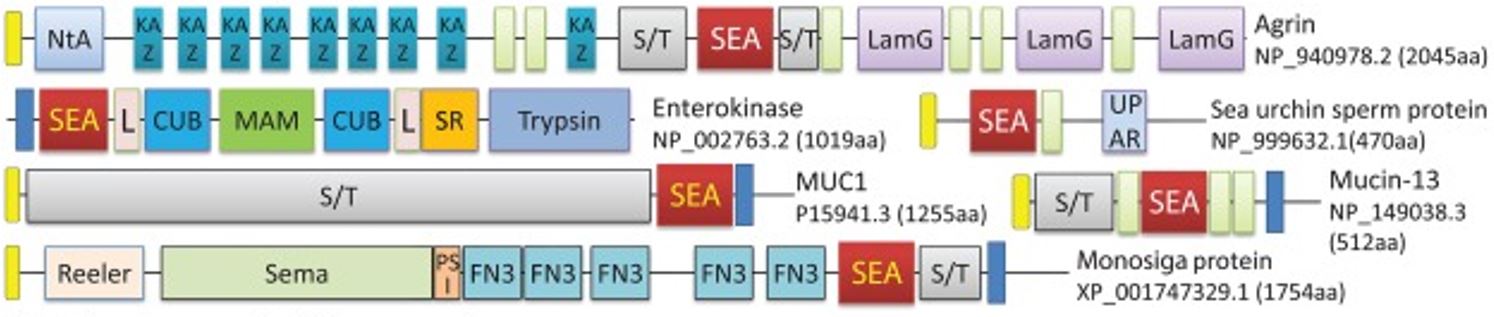
There are currently 3 agreed groups at this level the archaea domain bacteria domain and eukarya domain. It lists proteins with similar domain architectures and can retrieve proteins that contain particular combinations of domains. Many proteins consist of several domains.
Each domain contains a collection of organisms with similar properties and evolutionary histories as scientists have organized them. One domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may.
Each domain forms a compact folded three dimensional structure. Displays the functional domains that make up a given protein sequence. According to this system the tree of life consists of three domains.
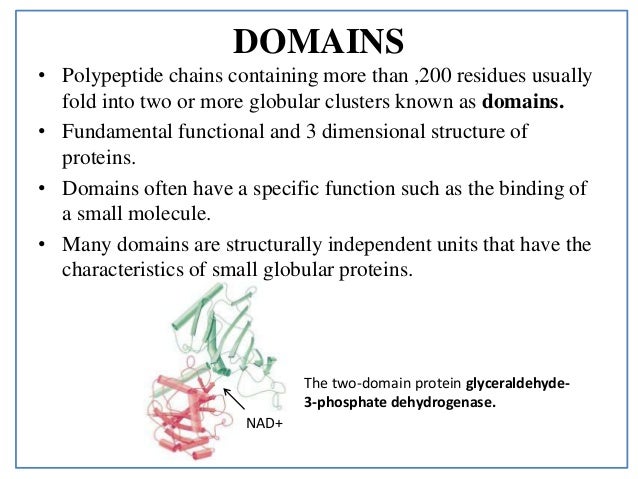
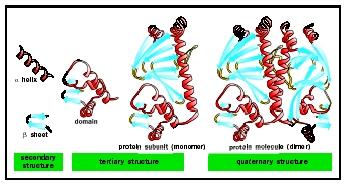
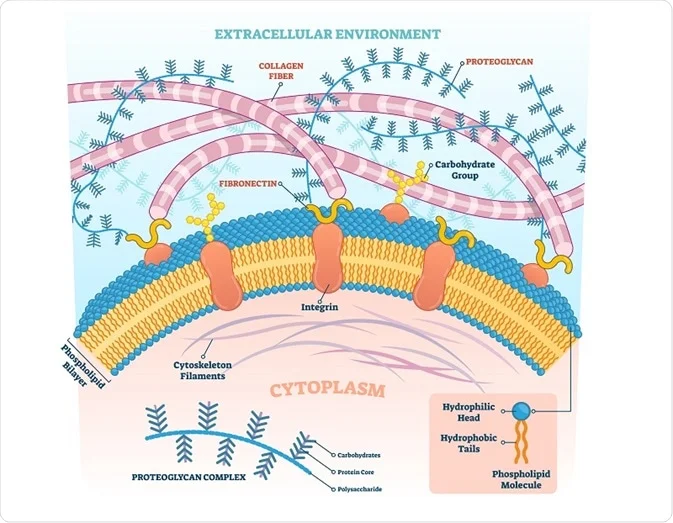
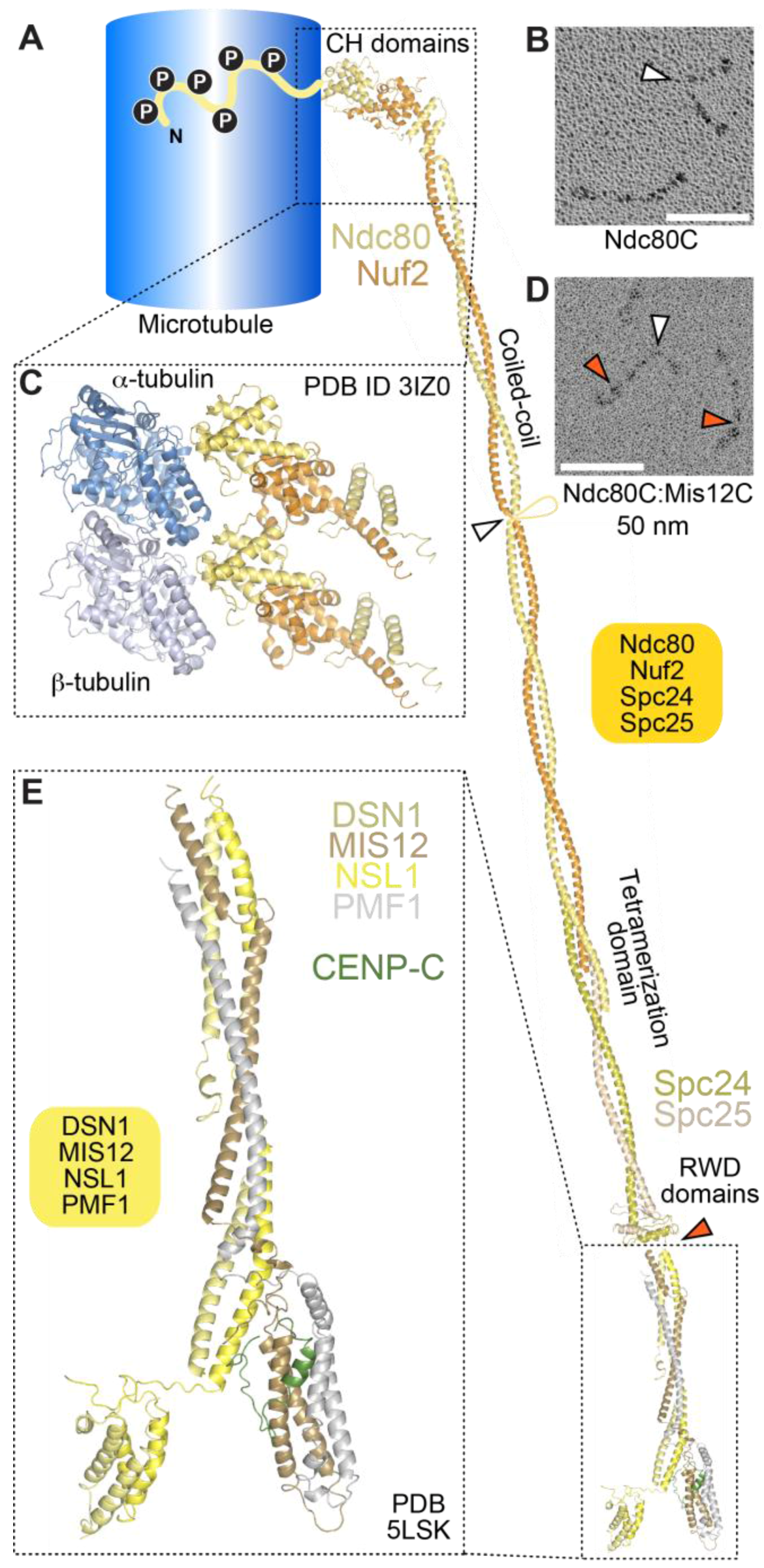
A protein domain is a region of the protein s polypeptide chain that is self stabilizing and that folds independently of the rest of the protein s polypeptide chain. In biological taxonomy a domain also superkingdom realm or empire is the highest taxonomic rank of organisms in the three domain system of taxonomy devised by carl woese et al.