Domain Name Hijacking Summary

The committee then presents.
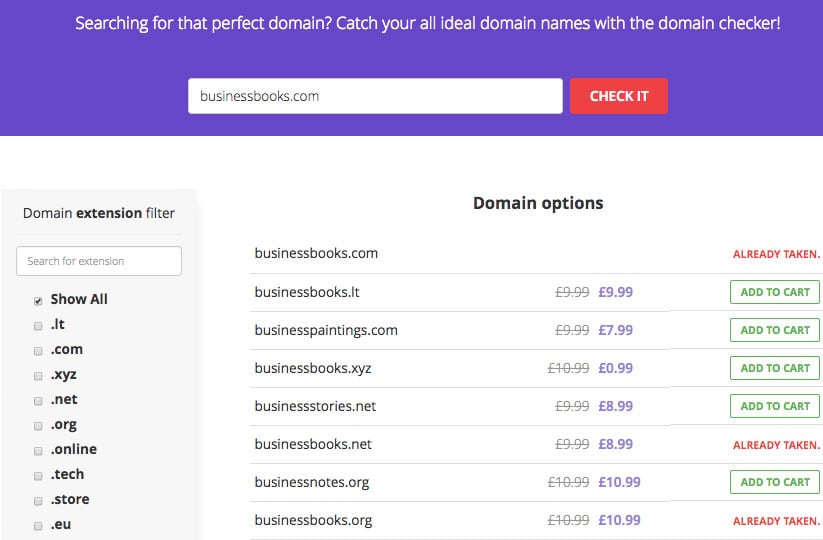
Domain name hijacking summary. Domain hijacking refers to the wrongful taking of control of a domain name from the rightful name holder. Name holders can take measures to protect their domain names against theft and loss but many measures are not generally. The common use of the term encompasses a number of attacks and incidents.
In most cases dns hacking is caused by a malware infection that alters the dns configuration on the user s computer or network device. Dns hijacking is the term given when an attacker intercepts the traffic being requested from a dns and redirects it to another website often with malicious intent. The common use of the term encompasses a number of attacks and incidents.
The committee then presents its findings and recommendations. This includes changing dns name servers setting up a new domain status and transferring the domain name. Where domain names were hijacked.
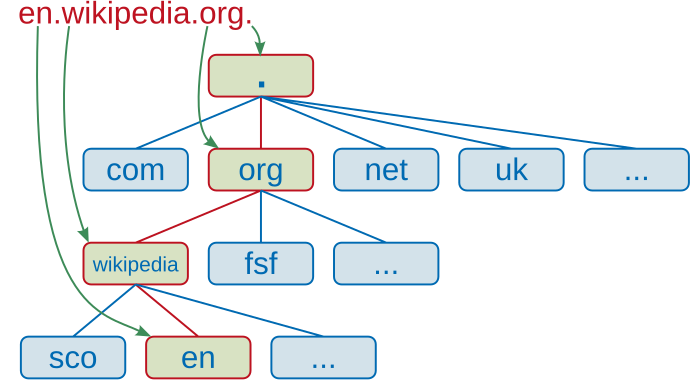
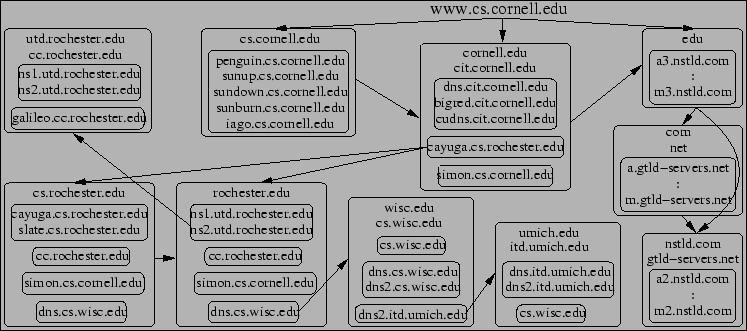
Incidents representative of common forms of attacks are discussed and analyzed in the report. Dns hijacking takes advantage of how the domain name system functions as the internet s phone book or more accurately a series of phone books that a browser checks with each book telling a. Domain hijacking refers to the wrongful taking of control of a domain name from the rightful name holder.
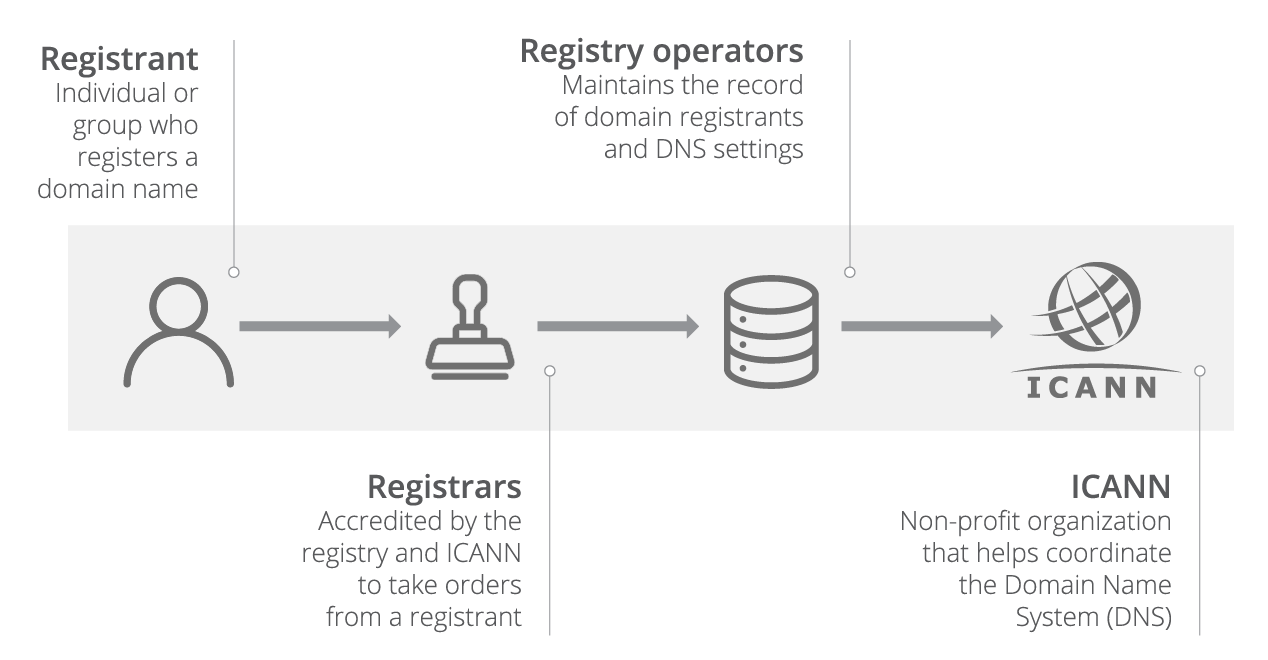
A hacker tries to get access to his target s complete domain registrar account details that will allow him to make unauthorized changes and transfers to his advantage. As a result the user s device communicates directly with a fake dns server instead of the real one and is then rerouted to a set of pre programmed malicious ip addresses. Domain hijacking or domain theft is the act of changing the registration of a domain name without the permission of its original registrant or by abuse of privileges on domain hosting and registrar software systems.
Domain hijacking is another way to say your domain name has been stolen. Incidents representative of common forms of attacks are discussed and analyzed in the report. When browsing the internet the requests to visit websites or make searches are sent to a domain name server dns which will direct the user traffic to the website requested.