Transmembrane Domain Biology Definition

Of a chromosome a region in which supercoiling occurs independently of other domains.
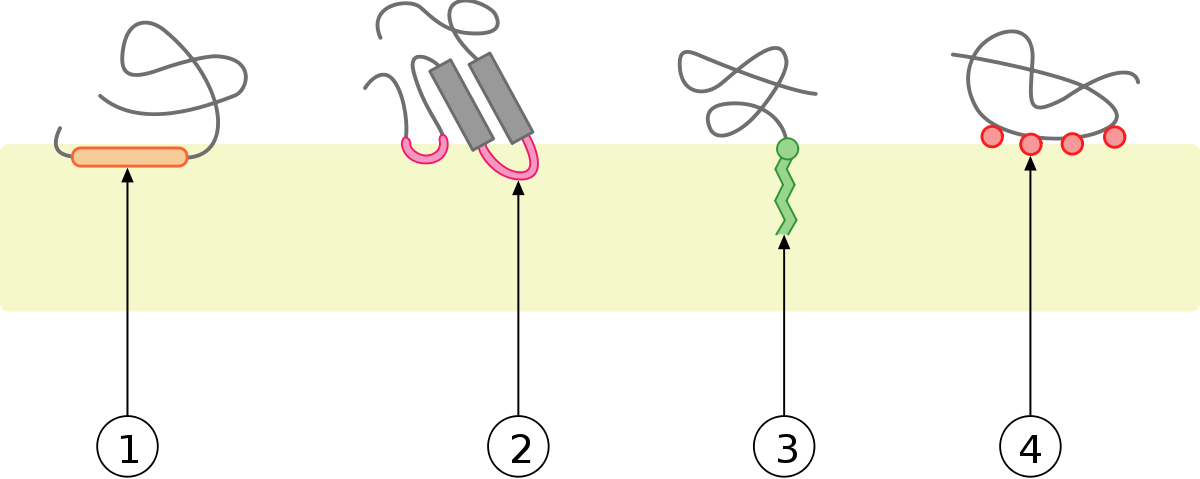
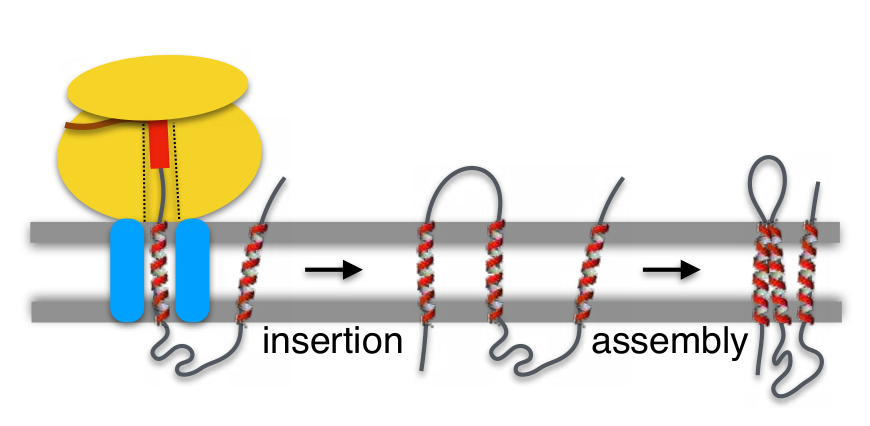
Transmembrane domain biology definition. A comprehensive reference 2008. Of a protein a discrete length of the amino acid sequence that is known to be associated with a specific function. A polypeptide sequence of about seven residues if sheet up to 22 residues if helix that connects extracellular to intracellular domains joined by extended polypeptides on the cytoplasmic and external or vesicular sides.
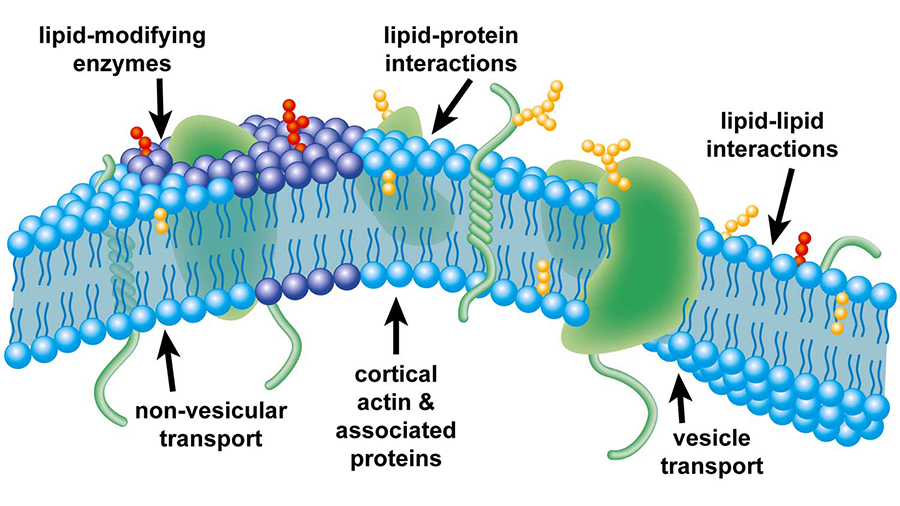
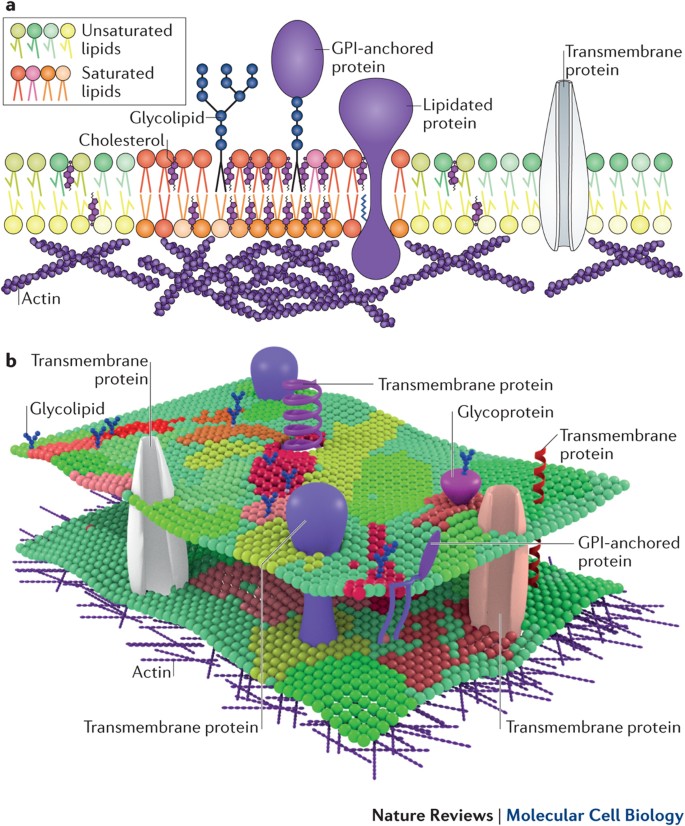
Transmembrane domains tmds are the hydrophobic areas or regions of the proteins. Transmembrane domain a feature of most intrinsic proteins of plasma or vesicular membranes. Since they are hydrophobic so they prefer to stay inserted inside the membrane of the cell.