Transactivation Domain Biology

In the context of gene regulation.
Transactivation domain biology. Receptor transactivation may result from the crosstalk of signaling cascades or the activation of g protein coupled receptor hetero oligomer subunits among. The transactivation domain or trans activating domain is a transcription factor scaffold domain which contains binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators. The full length p53 protein is the primary isoform expressed in human cells and this isoform is responsible for its tumor suppressor function.
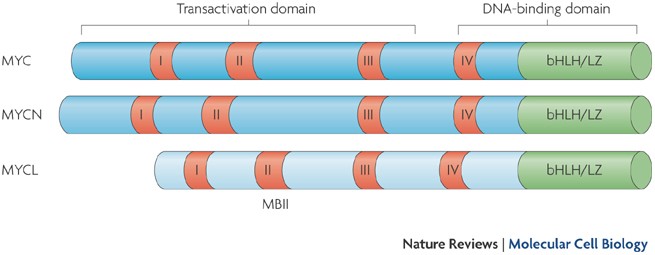
1 tads are named after their amino acid composition. These amino acids are either essential for the activity or simply the most abundant in the tad. The transactivation domain is located at the amino terminus of the protein sequence amino acids 1 73.
Tads are named after their amino acid composition. Transactivation domain last updated december 11 2019. In the context of receptor signaling transactivation occurs when one or more receptors activate yet another.
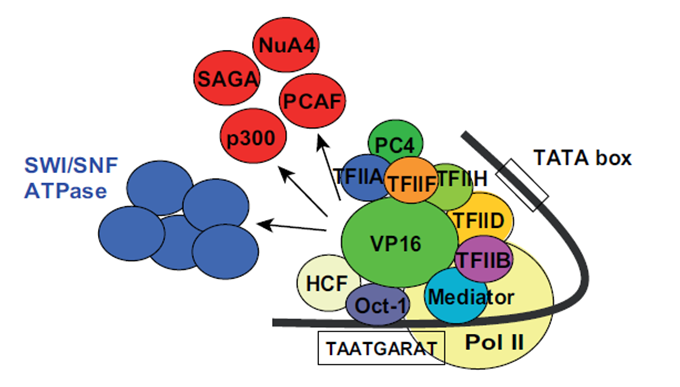
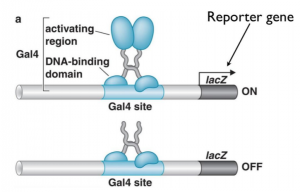
Transactivation by the gal4 transcription factor is mediated by acidic amino acids whereas hydrophob. Because the p53 gene contains multiple transcriptional start sites the p53 protein can either contain the transactivation domain denoted p53 or lack a full length transactivation domain figure 1 a. The transactivation domain or trans activating domain tad is a transcription factor scaffold domain which contains binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators these binding sites are frequently referred to as activation functions afs.
Transactivation is the increased rate of gene expression triggered either by biological processes or by artificial means through the expression of an intermediate transactivator protein.