Domain Meaning Proteins

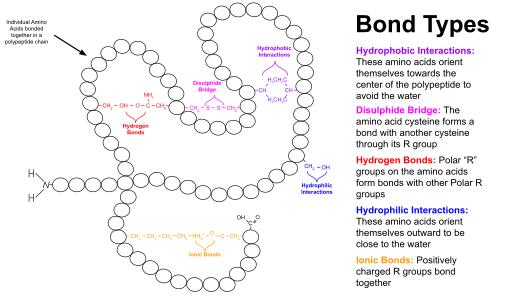
A protein domain is a region of the protein s polypeptide chain that is self stabilizing and that folds independently of the rest of the protein s polypeptide chain.
Domain meaning proteins. Multiple studies have demonstrated that domain domain interactions ddis are useful for predicting ppis since domains are directly involved in the intermolecular interactions memisevic et al. Like the ph domain above many domains are not unique to the protein products of one gene but instead appear in a variety of proteins. Each domain forms a compact folded three dimensional structure.
A structural domain is an element of the protein s overall structure that is stable and often folds independently of the rest of the protein chain. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may. Domains may exist in a variety of biological contexts where similar domains can be found in proteins with different functions.
Many proteins consist of several domains. Usually they are responsible for a particular function or interaction contributing to the overall role of a protein. Domains are distinct functional and or structural units in a protein.
Proteins sharing more than a few common domains are encoded by members of evolutionarily related genes comprising gene families.