Domain Math Term Definition

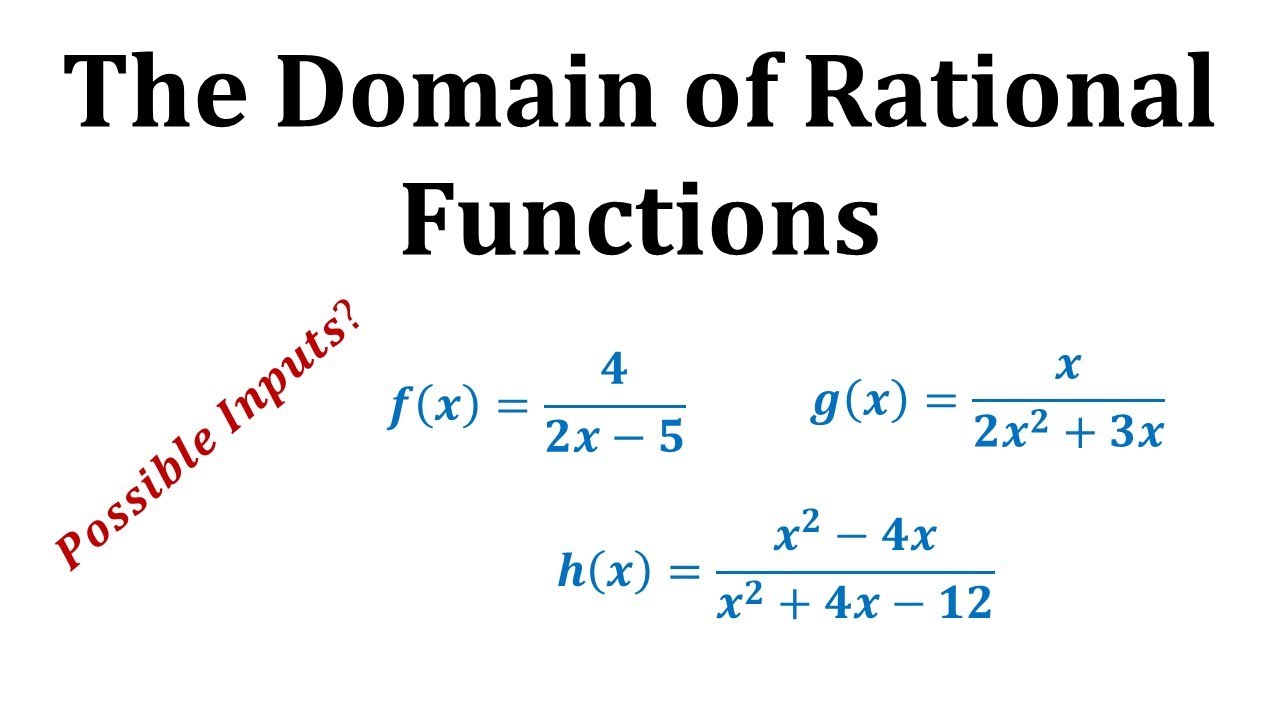
A simple mathematical function has a domain of all real numbers because there isn t a number that can be put into the function and not work.
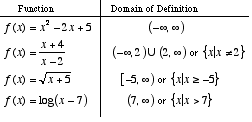
Domain math term definition. All the values that go into a function. The example below shows two different ways that a function can be represented. In mathematics the domain or set of departure of a function is the set into which all of the input of the function is constrained to fall.
It is quite common for the domain to be the set of all real numbers since many mathematical functions can accept any input. The set of values of the independent variable s for which a function or relation is defined. Domain in math is defined as the set of all possible values that can be used as input values in a function.
Usually domain means domain of definition but sometimes domain refers to a restricted domain. Domain function range. It is the set of all values for which a function is mathematically defined.
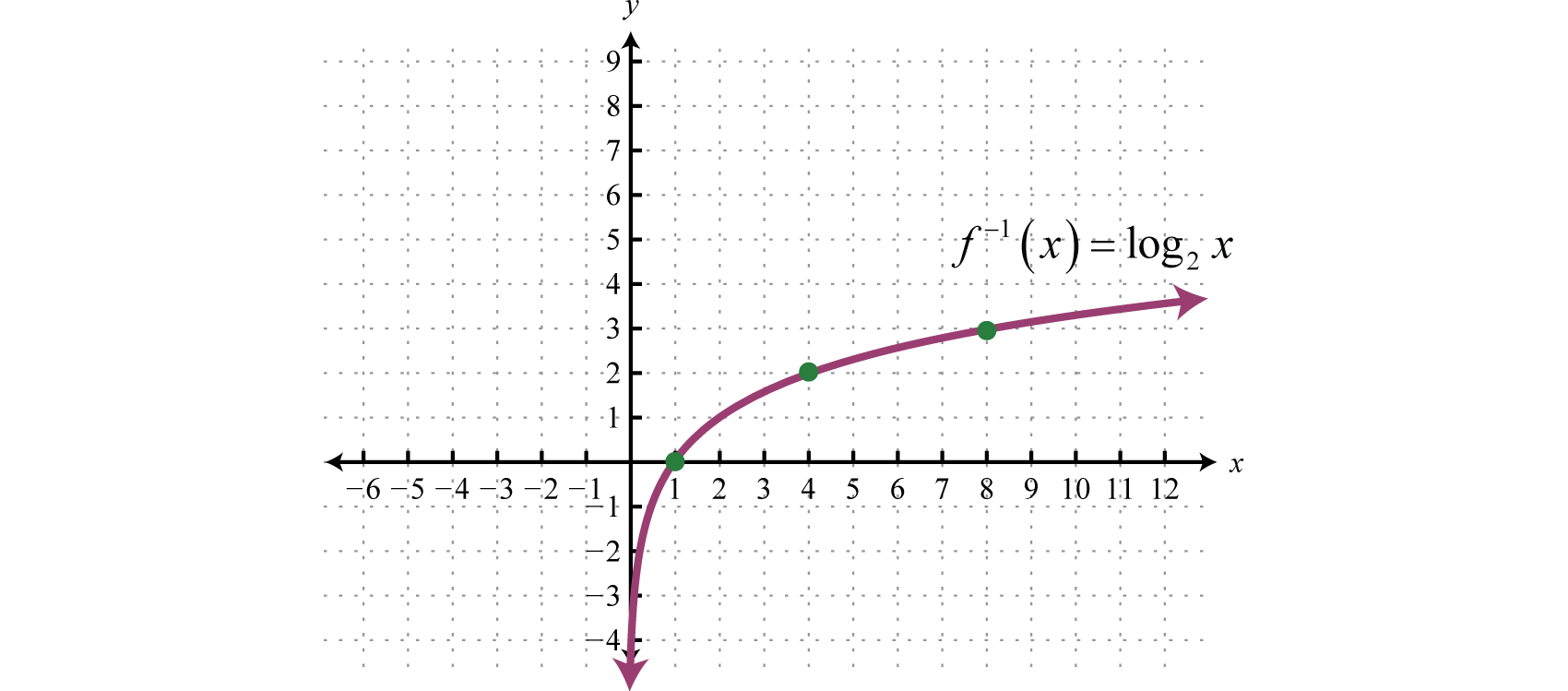
As a function table and as a set of coordinates. Domain definition the domain of a function is the set of its possible inputs i e the set of input values where for which the function is defined. The output values are called the range.
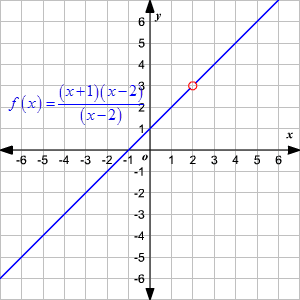
However this coincidence is no longer true for a partial function. Typically this is the set of x values that give rise to real y values. In the function machine metaphor the domain is the set of objects that the machine will accept as inputs.
When the function f x x2 is given the values x 1 2 3 then the domain is simply those values 1 2 3 domain range and codomain. It is the set x in the notation f. X y and is alternatively denoted as.