Domain Math Simple Definition

Domain of a function.
Domain math simple definition. Domain definition the domain of a function is the set of its possible inputs i e the set of input values where for which the function is defined. Domain in math is defined as the set of all possible values that can be used as input values in a function. In mathematics the domain or set of departure of a function is the set into which all of the input of the function is constrained to fall.
All the values that go into a function. X y and is alternatively denoted as. It is the set of all values for which a function is mathematically defined.
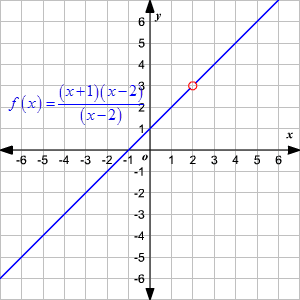
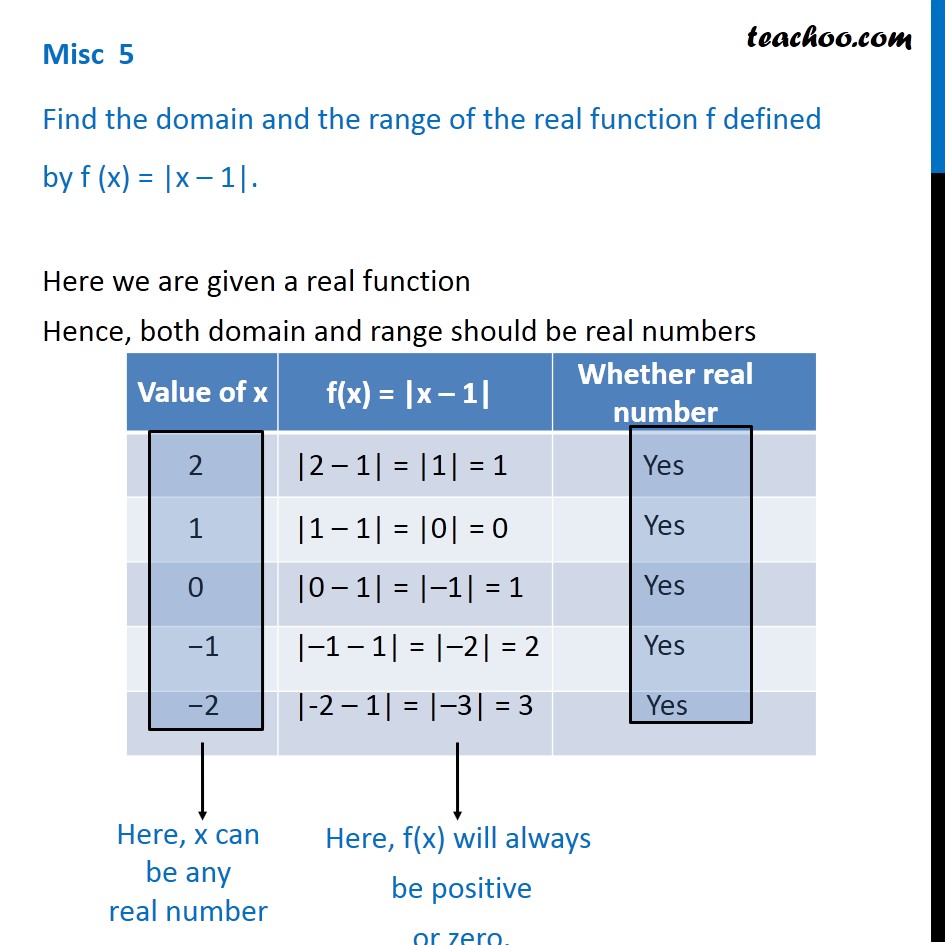
To find the domain of this function we need to remember the definition of a domain and then do simple algebra. Mathematics the set of all values that an independent variable of a function can have. It is the set x in the notation f.
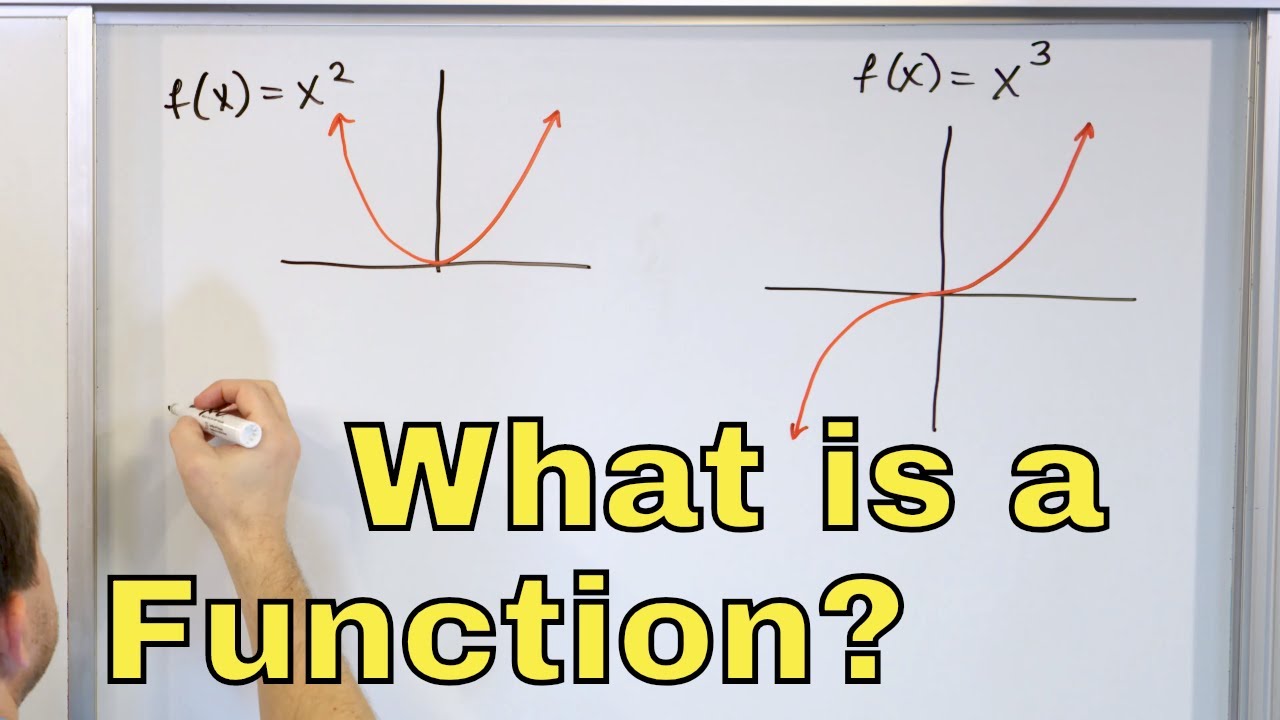
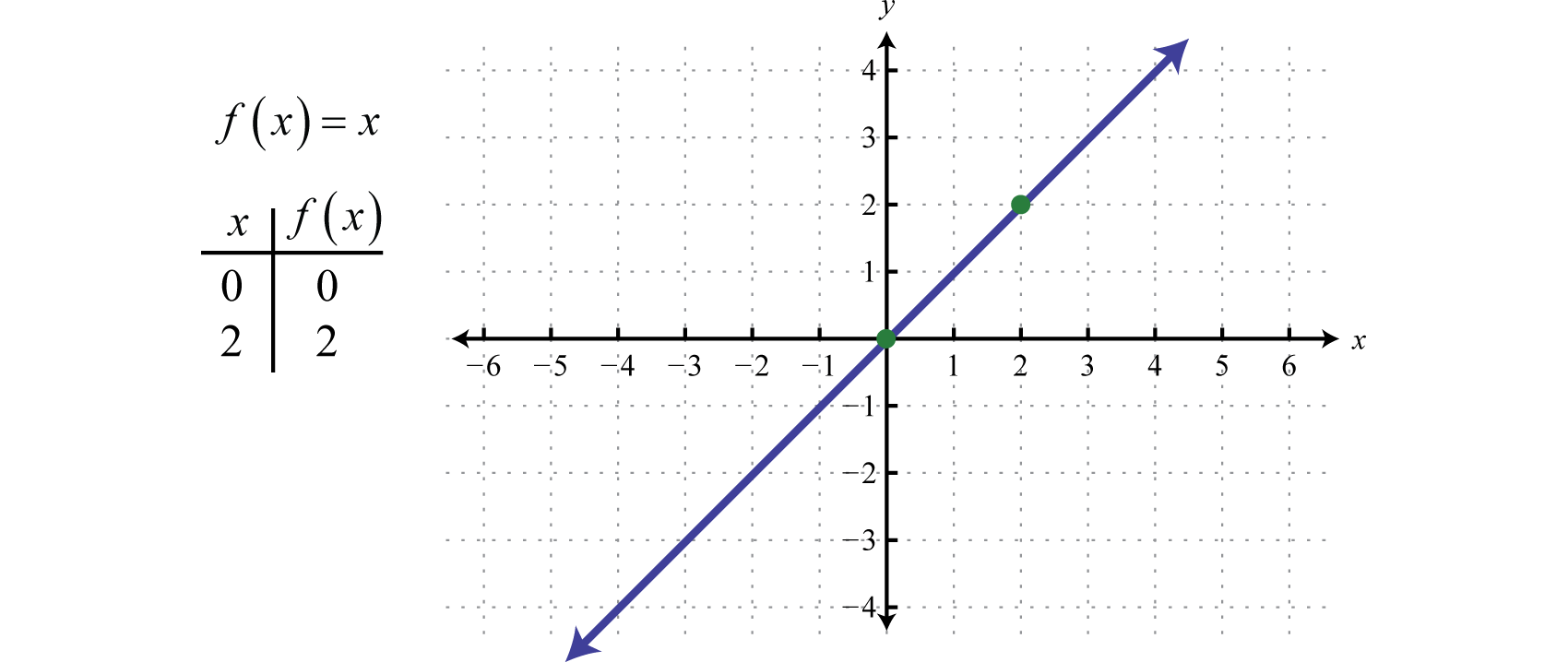
Math mathematics maths a science or group of related sciences dealing with the logic of quantity and shape and arrangement. When the function f x x2 is given the values x 1 2 3 then the domain is simply those values 1 2 3. In the function y 2x the set of values that x the independent variable can have is the domain.
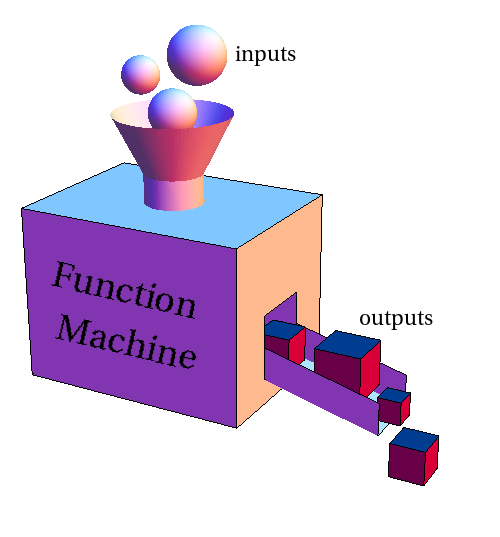
One thing we remember about the domain of a function is that it cannot include a. A domain in general computer terminology is also the range of values that belong to a specific attribute. In the function machine metaphor the domain is the set of objects that the machine will accept as inputs.
Domain function range. Within a google sheet the list of possible values that the user has designated for a specific column are that column s domain. A simple mathematical function has a domain o history.