Domain Differences Biology
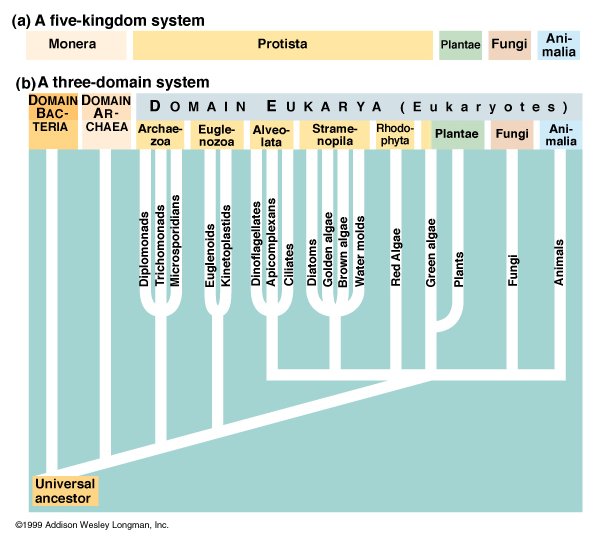
According to this system the tree of life consists of three domains.
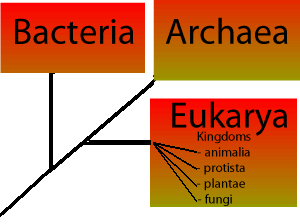
Domain differences biology. In biology a domain refers to the largest of all groups in the classification of life. Each of these three domains recognized by biologists today contain rrna which is unique to them and this fact in itself forms the basis of three domain system. There are currently 3 agreed groups at this level the archaea domain bacteria domain and eukarya domain.
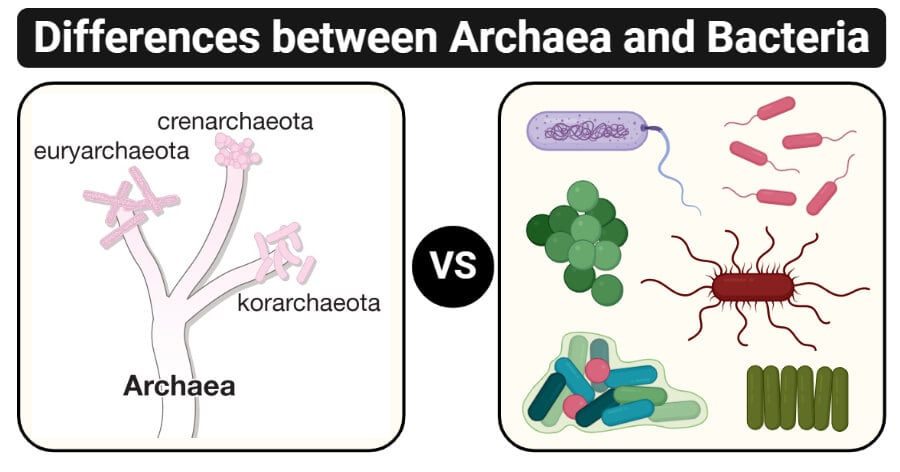
All life that has a cell nucleus and eukaryotic membrane bound organelles is included in eukar. The current three domain system groups organisms primarily based on differences in ribosomal rna rrna structure. While the presence of nuclear membrane differentiates the eukarya domain from archaea domain and bacteria domain both of which lack nuclear membrane the distinct biochemistry and rna markers differentiate archaea and bacteria domains from each other.
Organisms can be classified into one of three domains based on differences in the sequences of nucleotides in the cell s ribosomal rnas rrna the cell s membrane lipid structure and its sensitivity to antibiotics. Archaea bacteria and eukarya. In biological taxonomy a domain also superkingdom realm or empire is the highest taxonomic rank of organisms in the three domain system of taxonomy devised by carl woese et al.
Under this system organisms are classified into three domains and six kingdoms. The three domains are the archaea the bacteria and the eukarya.